Nutrition Tips to Prevent, Manage, and Reverse Fatty Liver Disease from a Long Island Dietitian
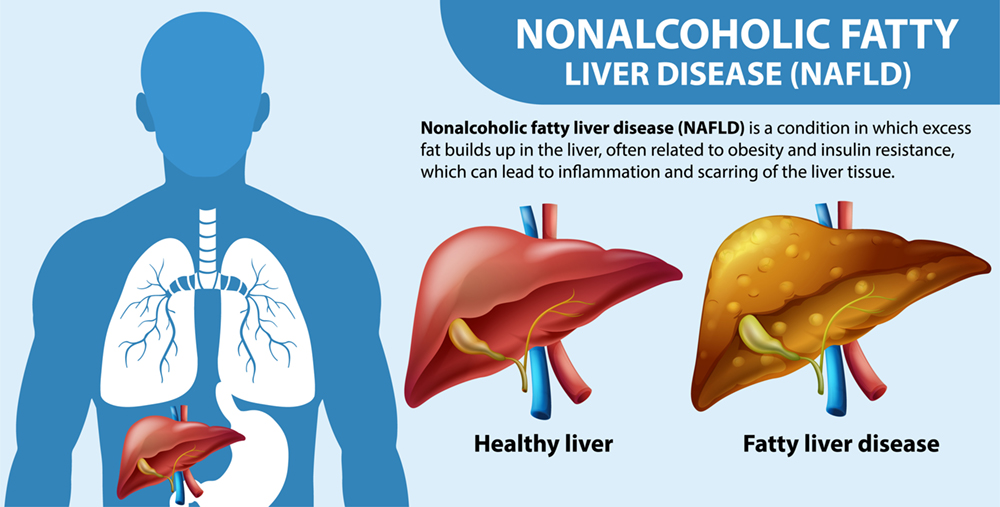
MASLD (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease) previously known as NAFLD (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease), is now recognized as the most common liver disease worldwide, affecting approximately 25% of the global population. Since Diet, Exercise, and an Optimal Weight are the cornerstones of treatment, by working with a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist you can learn to prevent, manage, and even reverse fatty liver.
It is important to understand the function of the liver. The biggest role is to filter your blood all day, every day to:
- Regulate many of the chemicals in the blood
- Excrete bile which carries waste products from the liver
- Process blood from the stomach and intestines – breaking down balancing and creating important
- Metabolize drugs into forms that are easier to use for the rest of the body.
More than 500 vital functions have been identified with the liver. Liver health has an impact on your overall wellness. And nutrition has a significant impact on liver health
Dietitian Recommendations to Improve Liver Health
Attain and Sustain your optimal weight
Attaining and maintaining an optimal weight is crucial in managing fatty liver disease. Excess body fat, particularly fat around the organs, is a major contributing factor. Losing weight can be the most effective way to reduce the fat that has accumulated in the liver, which in turn will improve liver health and potentially reverse the disease progression.
Establish a Mediterranean Style Pattern.
This is a balanced plan containing starch, lean protein, and vegetables at meals. The emphasis is on selecting minimally processed foods – avoiding ultra processed foods. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil, is particularly effective in managing fatty liver disease.
Reduce and/or Eliminate Alcohol Intake:
Alcohol may result in additional fat deposition in the liver, potentially increasing damage and therefore progression of liver disease. It can also lead to inflammation and scarring.
Decrease the Intake of Fat
Those with fatty liver disease need to limit their fat intake. Within a low-fat plan, reduce saturated and trans fats, and select unsaturated fats, especially omega-3 fatty acids.
Avoid Ultra processed Foods.
HFCS (high fructose corn syrup, simple sugar, added fructose sugars, can convert to liver fat.
Avoid Endocrine-Disrupting chemicals:
In my next blog, I will discuss what this means and where you find these chemicals and, most importantly, how to avoid them!
Managing a fatty liver with nutrition therapy is considered a primary treatment. Dietary changes and lifestyle modifications are the most effective way to manage fatty liver disease (NAFLD/MASLD), with a focus on weight management, limiting fats and ultra-processed foods, while incorporating a diet rich in fiber, lean protein, and healthy fats. Working with Registered Dietitian Nutritionist to develop your personalized plan may not only prevent but also reverse MASLD.